How can you protect yourself from pesticide exposure?
Pesticides are chemicals that are widely used to control pests and protect crops, gardens, and other areas from damage. However, exposure to pesticides can have negative effects on human health. Pesticide exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption, leading to a wide range of short- and long-term health effects. It is important to take necessary precautions to protect oneself from pesticide exposure. This article will provide an overview of ways to protect yourself from pesticide exposure, including wearing protective gear, following label instructions, avoiding exposure, proper storage, washing hands, choosing organic products, implementing integrated pest management practices, supporting regulations, and education. By taking necessary precautions to minimize exposure to pesticides, individuals can better protect themselves and their families from potential health risks associated with pesticide use.
Importance of Protecting Oneself From Pesticide Exposure
Protecting oneself from pesticide exposure is of utmost importance for several reasons. Pesticides are chemicals that are used to kill pests, including insects and weeds, in agricultural fields and other settings. While these chemicals can be effective in controlling pests, they can also pose a significant risk to human health if proper precautions are not taken.
Exposure to pesticides can lead to a range of health problems, from minor skin irritations to more serious conditions like cancer and neurological disorders. Long-term exposure to pesticides has also been linked to reproductive and developmental problems, as well as immune system dysfunction.

Credit: ensia.com
Recap of Ways to Protect Oneself From Pesticide Exposure
To recap, here are some ways to protect oneself from pesticide exposure:
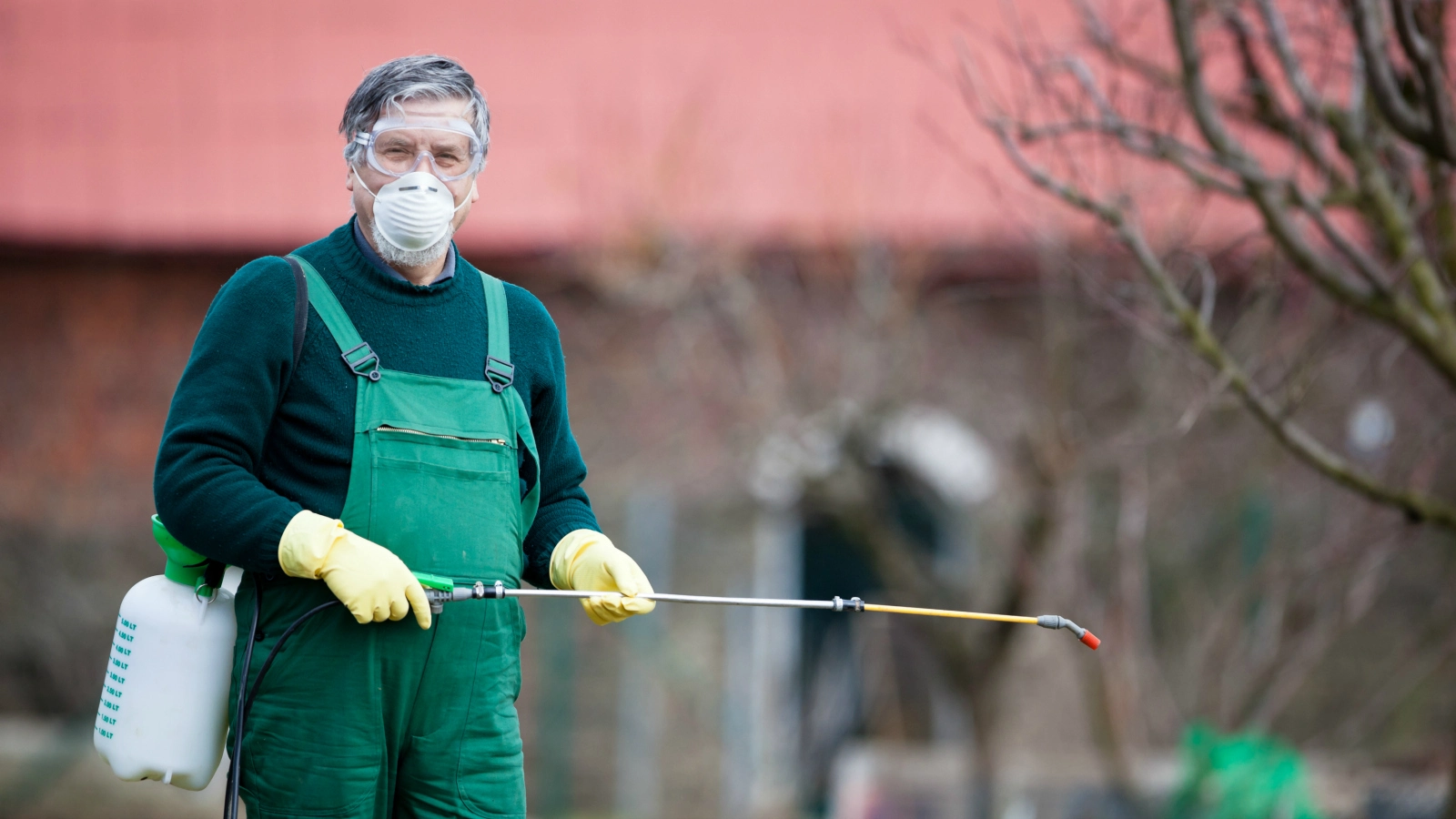
- Wear protective clothing and equipment when working with pesticides, such as gloves, goggles, and respirators.
- Follow all safety guidelines and instructions provided by the manufacturer when using pesticides.
- Properly store and dispose of pesticides to avoid accidental spills or leaks that could lead to exposure.
- Be mindful of the types of foods you consume and where they come from, as pesticide residues can linger on crops and make their way into the food supply.
- Avoid areas where pesticides have recently been applied, and stay out of fields or other settings where pesticides are being sprayed or used.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after handling pesticides or being in areas where pesticides are used.
- Consider using alternative pest control methods that do not involve the use of chemicals, such as natural predators or physical barriers.
Short- and long-term Health Effects of Pesticide Exposure
Pesticide exposure can have short- and long-term health effects on individuals. Short-term effects may include skin irritation, eye irritation, headache, dizziness, and nausea. These symptoms typically occur immediately after being exposed to pesticides or inhaling them.
Long-term exposure to pesticides can be more serious and may lead to chronic health problems. Some studies have linked pesticide exposure to cancer, neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, and reproductive problems. Prenatal exposure to certain types of pesticides has been shown to be particularly harmful to the developing brains of fetuses and young children, leading to cognitive and behavioral problems that can persist into adulthood.
Exposure to pesticides can also affect the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and other illnesses. In addition to the risks posed to human health, pesticides can also have negative effects on the environment, including the poisoning of wildlife, contamination of soil and water sources, and destruction of ecosystems.
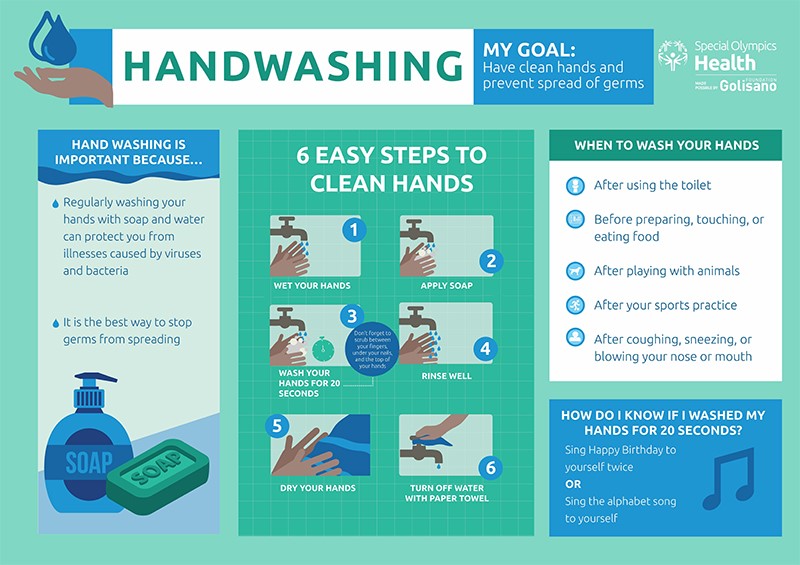
Proper Hand-Washing Techniques
Proper hand-washing techniques are essential for preventing the spread of germs and avoiding illness. Here are the steps to follow:
- Wet your hands with clean running water, warm or cold.
- Apply soap and lather your hands by rubbing them together with the soap. Be sure to lather the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
- Scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds.
- Rinse your hands well under clean, running water.
- Dry your hands using a clean towel or air-dry them.
Credit: www.specialolympics.org
Precautions to Take When Using Pesticides
When using pesticides, it’s important to take several precautions to minimize the risk of harm to yourself and others. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Read the label and follow all instructions: Pesticides should be used exactly as directed on the label. Follow all safety instructions carefully to avoid accidents or exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Wear protective clothing and equipment: This may include gloves, goggles, long-sleeved shirts, and pants, as well as a respirator or mask if necessary.
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes: If you get pesticide on your skin, wash immediately with soap and water. Flush your eyes with clean water for at least 15 minutes if they come into contact with pesticides.
- Handle and store pesticides properly: Keep pesticides in their original containers and always label them clearly. Store pesticides in a secure, dry location that is out of reach of children and pets.
- Don’t smoke, eat, or drink while handling pesticides: These chemicals can be absorbed through the mouth and lungs and potentially cause harm.
- Dispose of pesticides safely: Do not dispose of pesticides in the trash or pour them down the drain. Contact your local solid waste agency or environmental health department for guidance on proper disposal methods.
- Ventilate the area: Open windows and doors to allow fresh air to circulate when using pesticides indoors.
By taking these precautions, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of exposure to pesticides and protect their health and the environment.
Importance of keeping pesticides out of Reach of Children and Pets
It is vitally important to keep pesticides out of reach of children and pets because they are more vulnerable to the harmful effects of these chemicals than adults. Children and pets may be more likely to touch, ingest, or inhale pesticides due to their curious nature and tendency to explore their environment.
Pesticides can cause serious health problems if ingested or absorbed through the skin, including poisoning, respiratory problems, and neurological damage. Children and infants are especially at risk, as their bodies are still developing and they may not be able to metabolize or excrete toxins from their systems as effectively as adults.
Pets are also susceptible to pesticide exposure, which can lead to a range of health issues, including vomiting, diarrhea, seizures, and even death. Small animals like birds and fish are particularly sensitive to pesticides and can be affected even by small amounts.

Credit: interstateproducts.com
Reducing Pesticide Exposure Through Organic Choices
One effective way to reduce pesticide exposure is by making organic choices. Organic foods are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers, which can significantly reduce the number of chemical residues present in these foods.
By choosing organic options for fruits, vegetables, and other foods, individuals can lower their risk of exposure to harmful chemicals and potentially reduce the risk of health problems associated with pesticide exposure. In addition to reducing exposure to pesticides, organic farming practices can also promote biodiversity and soil health, leading to healthier ecosystems overall. Organic products can be identified by labels such as “USDA Organic” or “Certified Organic”, which indicate that the food has been produced according to strict standards for organic farming and processing. While organic foods may be more expensive than conventional options, many people consider the benefits to outweigh the cost.
Conclusion
protecting oneself from pesticide exposure is essential for maintaining good health and preserving the environment. Pesticides can have both short-term and long-term health effects on individuals, and can also have negative effects on the environment. To protect oneself from pesticide exposure, it is important to take several precautions such as wearing protective clothing and equipment, following safety guidelines and instructions provided by the manufacturer, and properly storing and disposing of pesticides. It’s also important to be mindful of the types of foods consumed and where they come from, as pesticide residues can linger on crops.
Reducing pesticide exposure through organic choices is another effective strategy for promoting health and sustainability. By making informed decisions about what we eat and how it is produced, we can help protect our bodies and the environment from the potentially harmful effects of pesticides.